Long-term success isn’t just about growth – it’s about building the right team, setting up strong processes, and shaping a culture that supports your mission. This chapter will help you get your startup ready for the next phase of growth – while staying agile and competitive.
This section is for you if …
- you’ve founded an impact startup.
- your target group, problem, solution, and impact are clearly defined.
- your minimal viable product (MVP) has been tested and validated.
- you’ve mapped out your impact potential, market opportunity, and funding model.
- you have the resources in place to grow.

Not quite there yet?
Check out the section that fits your current stage
In this section, you’ll learn how to …
- grow and develop your team with intention.
- build efficient structures and processes.
- reflect on and shape your organizational culture.
Build and strengthen your team
As your startup scales, having the right team in place is essential. That means more than just hiring – it also means investing in the people you already have. Ask yourself: What skills are missing? And how can you close those gaps? A clear plan for skill-building, team development, and smart recruitment sets the stage for long-term, mission-driven growth.
1. Pinpoint the skills you need
Start by identifying the key skills required for each role on your team. Consider both hard skills (technical know-how) and soft skills (communication, leadership, etc.), keeping your long-term goals in mind.
Common hard skill gaps:
- Technical skills: Limited coding or AI knowledge can hold back product development.
- Financial skills: Weaknesses in budgeting or accounting can put your startup’s future at risk.
- Project management: Without clear planning and execution, your team’s efficiency takes a hit.
- Impact measurement: If you can’t measure and track your social or environmental impact, it’s tough to show results.
Common soft skill gaps:
- Teamwork or communication issues can strain collaboration – internally and with users or target groups.
- Limited creativity or problem-solving can stall innovation and slow momentum in tackling challenges.
- Lack of leadership or management skills can disrupt workflows, team dynamics, and your culture.
Bring on an impact lead
Set up a dedicated role to track and steer your startup’s impact. You don’t always need to hire someone new.
You just need to make sure someone on your team has the time and tools to take it on.
Strong impact management helps you stay focused, show results to investors and stakeholders, and improve your solution over time. It’s also becoming a must-have for standing out in a crowded market.
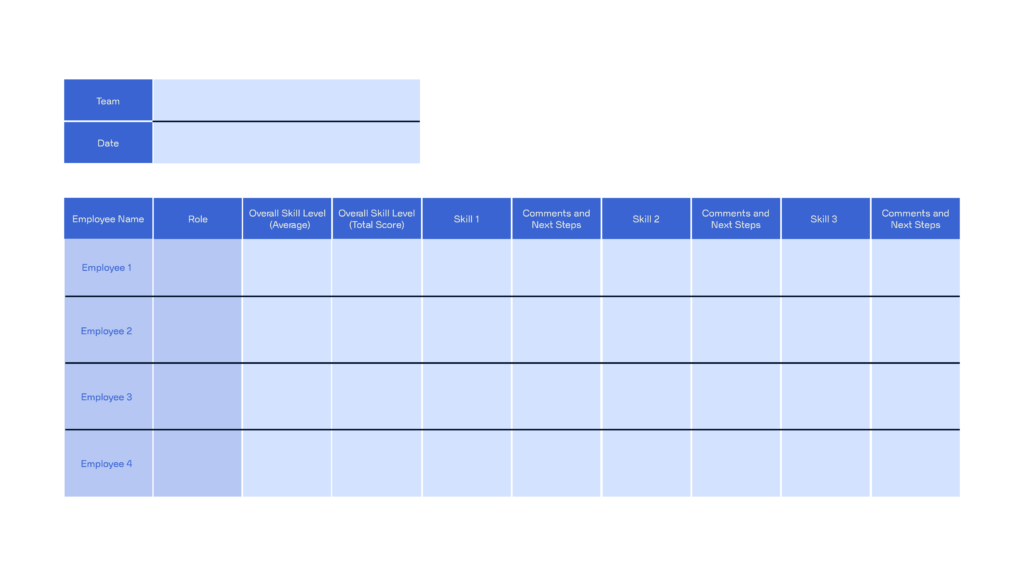
2. Take stock of your team’s skills and spot the gaps
Once you’ve mapped out the skills your startup needs, it’s time to see what your team already brings to the table. You can do this through performance reviews, self-assessments, or informal check-ins.
A skills matrix can help you match your team’s current strengths with what’s actually needed. Use it to identify the most important gaps – and focus on those first.
3. Dig into the root causes and impact of those gaps
Figure out what’s behind the missing skills. Then look at how those gaps are holding your team back – from missed goals to slow progress.
4. Build a practical action plan
Then put together a clear plan. This might mean offering targeted training, hiring new people, or both. Set achievable goals and timelines.
Get clear on processes and responsibilities
When workflows are fuzzy and roles aren’t defined, things can fall through the cracks. By streamlining your processes and clearly assigning responsibilities, you make teamwork smoother, boost transparency, and lay the groundwork for steady, sustainable growth.
1. Pick a process to analyze
Choose one core process in your startup to focus on, and define clear starting and ending points. Ask yourself: What steps are truly necessary? Who’s responsible for what? And how does this process affect your overall impact? Some examples of key processes include:
Product development
Marketing
Procurement
Sales
Impact management
Meetings
Feedback and review
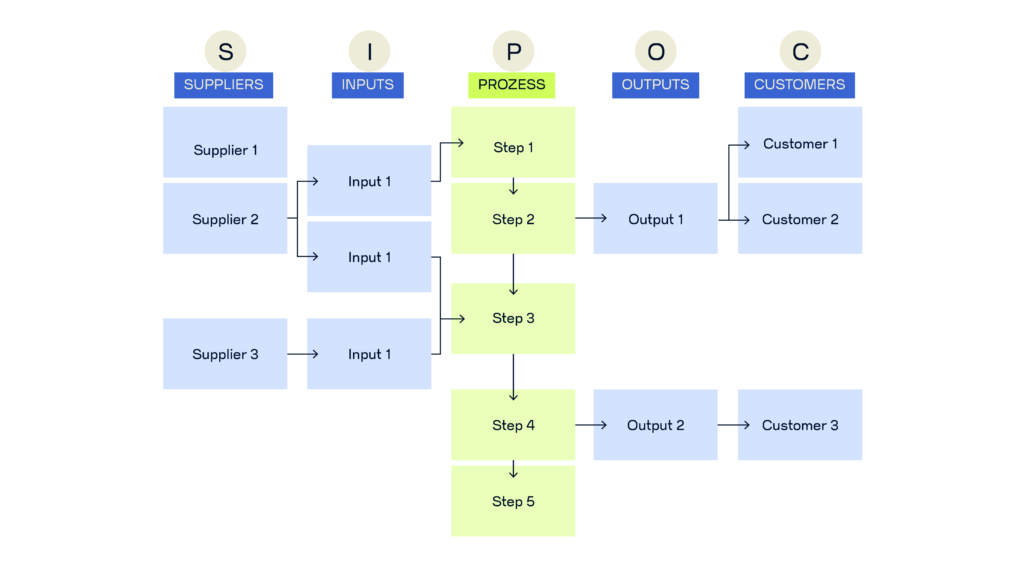
2. Use a SIPOC diagram to map it out
A SIPOC diagram is a simple way to visualize and break down a process. It helps you understand the key elements and pinpoint what drives success – or where improvements are needed. SIPOC stands for:
- Suppliers: Who provides the inputs for this process? This could be external partners, internal teams, or other stakeholders.
- Inputs (resources): What materials, tools, or information are needed to get the process started?
- Processes: What are the key steps, from beginning to end? Focus on listing five to seven main steps in order.
- Outputs (results): What’s the end result of the process? This could be a product, service, report, or any other deliverable.
. - Customers (clients): Who receives or benefits from the output? This could include external clients, internal teams, or anyone who relies on the results.
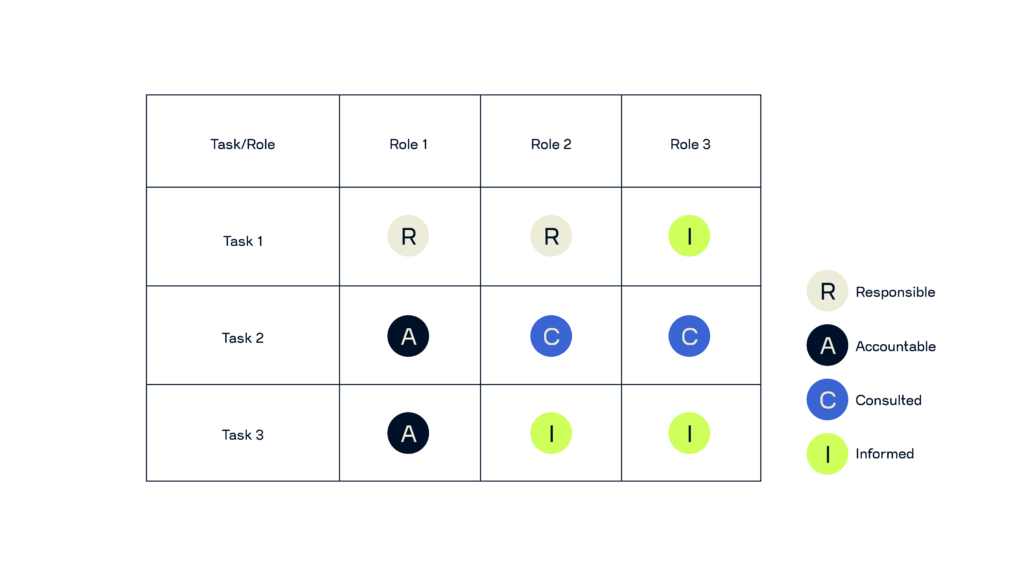
3. Take a closer look at each activity in the process
Document every task needed to carry out the process from start to finish. To clearly define who’s doing what – and improve efficiency – you can use the RACI method. RACI helps clarify roles by assigning each task to one or more of the following categories:
- Responsible: Who is directly responsible for completing the task? There can be more than one responsible person, but try to keep it manageable.
- Accountable: Who has final ownership of the task? Each task should have just one accountable person.
- Consulted: Who should be asked for input? These people should be involved before key decisions are made.
- Informed: Who needs to stay in the loop? These people aren’t directly involved but should be kept up to date.
4. Check how each activity affects your impact
Every action you take can influence your startup’s social, environmental, or economic impact – positively or negatively. To make sure you’re using your resources wisely, take the following steps:
Evaluate how each activity affects your impact an to what extent. Use clear ata an KPI tracking (regular measurement of key values). Use your systems map from the “Impact management” / LINK) to spot unintended side effects. This includes negative outcomes from your business model an your behavior across your the entire value chain (see note). Once you identify weak points, create targeted measures to eliminate them.
ESG management
Want to improve how you manage ESG (environmental, social, and governance) factors in your processes? You’ll find practical criteria to guide your approach here.
You can also explore whether a Social Life Cycle Assessment (S‑LCA) is right for your solution. This method helps you understand and evaluate the social and socioeconomic impacts of your product or service across its entire life cycle. S‑LCA gives you a clearer picture of where to make improvements and helps you move toward more sustainable and responsible production and consumption. Learn more about it here.
Reflect on your organizational culture
Your corporate culture is the backbone of your startup. It shapes how your team works together and how others see you. A strong, intentional culture can drive innovation, attract great talent, and bring your vision to life.
1. Define your core values
Think about what really matters to you – values like transparency, sustainability, or bold thinking – and how those values show up in your work. Bring your team into the conversation with workshops or brainstorming sessions to build a shared set of values that feel authentic and relevant. Aim for three to five core values that reflect who you are and what you stand for. Keep them focused, practical, and tailored to your startup – not just buzzwords.
2. Map out the culture you want
Start by taking stock of your current culture. Use anonymous surveys, one-on-one feedback, or team interviews to get honest input. Then ask: What kind of culture do we want to build? What will help us grow and stay true to our mission? Think about how you want people to collaborate, make decisions, and embody your values day to day.
Ask yourselves: What goals do we have? What needs to change? What makes strategic sense?
Think about how you want people to collaborate, make decisions, and embody your values day to day. Your ideal culture should support your goals, reflect your strategy, and fit your current challenges. To guide the process, try using the keep-start-stop method:
- Keep: What should be retained?
- Start: What should be started?
- Stop: What should be left behind?
3. Bring your organizational culture to life
Defining your values is just the first step – what matters most is how they show up in day-to-day decisions and behavior. For example, if one of your values is sustainability, that might mean choosing to work with environmentally responsible suppliers. Every decision you make should reflect your values, even as your startup grows or conditions change. Create a clear, inspiring vision for the culture you’re aiming for, such as: “We’re building a culture that encourages open feedback and embraces innovation.”
To track your progress, set measurable goals using the S.M.A.R.T. method.
Your goals should be:
- Specific: Clearly stated and well defined
- Measurable: Quantifiable
- Achievable: Realistic given your current resources
- Relevant: Aligned with your strategic goals
- Time-bound: Tied to a clear deadline
4. Put it all into a code of conduct
Turn your values and culture into a written code of conduct that everyone on your team can understand and follow. Have it reviewed by your legal team or external legal counsel. Make sure the document is easy to access – for employees and external partners – and available in all relevant languages. Hold regular training sessions to help your team understand how to apply the code in real-world situations.
Tip:
Your impact handbook should be a key part of your code of conduct. For more on how to create one, check out the chapter “Scaling your impact: strategy, validation, and growth for startups.”
Next step: Strategies for sustainable growth
You’ve started building a team that’s ready for growth, put smart systems in place, and laid the foundation for a strong organizational culture.
Before you dive into KPI tracking or create a baseline for measuring your impact, take time to develop strategies for sustainable growth and fine-tune your impact management strategy.